Chilean policies aimed at reining in unhealthy food marketing are succeeding in protecting children from the onslaught of television advertisements (TV ads) for these products, according to new research. The country’s multi-phased regulations, which began in 2016, have led to a 73% drop in children’s exposure to TV ads for regulated foods and drinks (those that exceed legal thresholds for calories, sugar, salt or saturated fat) by 2019. During this time, the number of ads for unhealthy foods dropped 64% on all TV programs and 77% during children’s programming. Researchers also found that 67% fewer unhealthy food ads used child-directed creative content such as cartoons, characters, toys or contests, which are also prohibited under the country’s laws.
These and other findings from researchers at the University of Chile, Diego Portales University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill underscore both the potential and need for strict rules around marketing to build healthier eating habits. The study also highlights the importance of a key policy addition contributing to the regulations’ success: The initial Law of Food Labeling and Advertising in 2016 limited child-directed creative content in any marketing and prohibited companies from placing TV ads for regulated products during programs attracting a child audience. In 2018, Chile extended this prohibition to a full “daytime” ban across all TV from 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. While researchers saw a decline in advertising for unhealthy foods during earlier phases of the law (in 2017 and early 2018), the significantly greater drop following the full daytime ban is noteworthy.
Key findings:
- Total TV advertising dropped 64% for unhealthy foods and drinks (i.e., those high in calories, sugar, salt and/or saturated fat) from 2016 (pre-regulation) to 2019, after the full 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. ban began.
- TV advertising for unhealthy products during children’s programming dropped 77%
from 2016 to 2019.
- Children viewed 73% fewer TV ads for regulated products in 2019 compared to 2016.
- The number of TV ads for unhealthy foods and drinks that used prohibited child-directed content (e.g., cartoon characters, prizes, games) dropped 67% from 2016 to 2019.
- For all outcomes, impacts were significantly greater after the full 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. daytime advertising ban began in 2018 compared to earlier restrictions during children’s programming, only (in 2017 and early 2018).
“Focusing on child-directed ad content and child-directed programming to reduce children’s exposure to unhealthy food advertising does work to an extent, based on what we’ve seen in Chile, but children are simply exposed to much more than this,” said Francesca Dillman Carpentier, PhD, W. Horace Carter Distinguished Professor at the UNC Hussman School of Journalism and Media and the study’s first author. “To markedly reduce the amount of unhealthy food promotions children view, we see that it takes a bold move like Chile’s 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. ban to be effective. The number of unhealthy food ads on TV, as well as kids’ exposure to them, was greatly reduced after Chile added the daytime ban on these ads.”
This study’s findings underscores a weakness of nearly all governmental restrictions on TV advertising for unhealthy foods worldwide: Most focus on very narrow windows of time or programming, leaving children exposed most of the day and night to targeted ads for unhealthy foods and drinks. (See below.) This study provides evidence that countries could significantly strengthen existing policies by expanding TV restrictions to complete bans. Countries considering introducing policies to regulate food marketing can also learn from the Chilean experience to protect children more effectively from ad exposure.
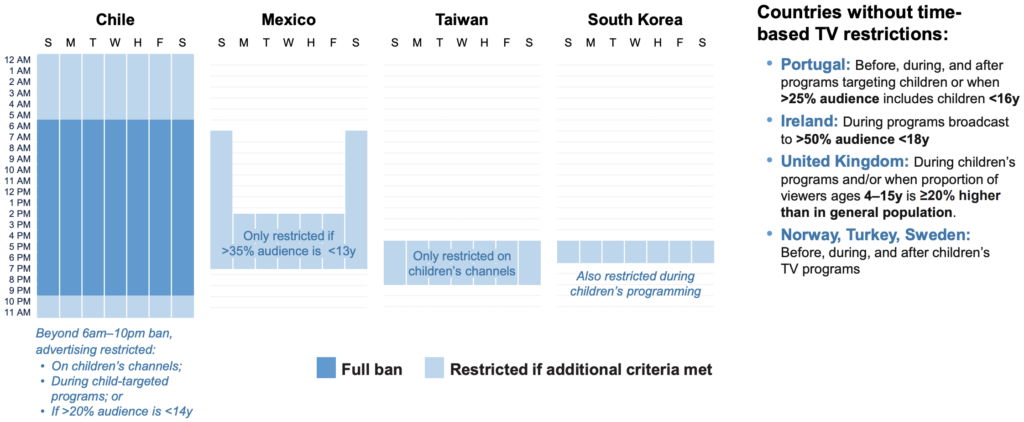
Chile enacted marketing controls in 2016 as part of an ambitious, comprehensive policy package aimed at reducing childhood obesity and other health risks by creating a healthier food environment. The Law of Food Labeling and Advertising also mandated “stop sign” warning labels on packages for unhealthy foods and banned their sale or promotion in schools. This remains one of the most ambitious regulatory frameworks in the world aimed at tackling rising nutrition-related diseases and soaring health care costs, and many policymakers and public health advocates worldwide have been watching to gauge the policy package’s effectiveness.
Other studies evaluating the combined effects of Chile’s marketing restrictions, warning labels and school ban have yielded similarly promising results: A study of household grocery purchases found a 24% drop in calories purchased in the first year (during the most lax period of the law’s three-phased nutritional criteria) and a 37% reduction in sodium purchased. Focus groups indicate that parents are being encouraged by their children to avoid buying foods with warning labels. Students reduced their sugar, saturated fat and sodium intake in schools — albeit with some evidence of compensation outside of school settings. And marketing restrictions also led to the removal of child-directed marketing strategies from nearly half of all “high-in” breakfast cereals to just 15% in the first year of the law.
“The Chilean experience has shown us that rigorous food marketing regulations work to reduce kids’ exposure to TV food advertising,” said co-author Lindsey Smith Taillie, PhD, associate professor and associate chair of academics in the Department of Nutrition at UNC-Chapel Hill’s Gillings Global School of Public Health.
“Looking to the future, we need to figure out how to monitor and regulate the digital food marketing environment, as kids increasingly shift their attention to smartphones and other online content.”
Key messages:
- Restricting advertising and creative marketing techniques for unhealthy foods and drinks protects children from harmful food marketing on TV.
- Banning advertising during all times when children might watch TV and across all channels and programs works significantly better than restricting advertising only during children’s programming.
- While this study finds marked and meaningful declines in children’s exposure to harmful food marketing on TV, some regulated products continued to advertise during restricted times or programs and using prohibited child appeals. There is room for improvement in policy enforcement to ensure industry compliance.
- This and other studies confirm that Chile’s policies are reducing harmful food marketing on television and food packages. Policymakers’ next challenge will be addressing the huge growth in food marketing in digital and social media.
This research was supported primarily by Bloomberg Philanthropies at part of the Food Policy Program, with additional support from INTA-UNC, INFORMAS, and CONICYT Fondecyt.
AUTHORS
Francesca R. Dillman Carpentier
Fernanda Mediano Stoltze
Marcela Reyes
Lindsey Smith Taillie
Camila Corvalán
Teresa Correa
Read the study in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity
RESOURCES

Read more about the evidence for restricting marketing for non-essential foods and drinks high in sugar, salt, saturated or trans fats, or calorie density.

Compare existing policies around the world aimed at restricting unhealthy food marketing to children.
MORE RESEARCH FROM CHILE:
After Chile’s labeling and marketing law, drink purchases contained less sugar and more non-nutritive sweeteners, but overall sweetness stayed the same Read more…
Study shows Chilean policy package led to declines in purchased calories, sugar, fat, and sodium Read more…
Study finds no negative economic impact from Chilean food labeling and advertising law Read more…
Sugary Drink purchases plunge following Chile’s new food law Read more…
